Zyvolux Insights
Exploring the latest trends and information for a better understanding of the world.
GPS: Your Unseen Navigator in the Digital Jungle
Navigate the digital jungle effortlessly! Discover how GPS technology guides you to success in the online world. Click to explore!
How GPS Technology Transforms Navigation in Our Everyday Lives
GPS technology has revolutionized the way we navigate our daily lives, making it easier than ever to find our way in an increasingly complex world. Gone are the days of unfolding paper maps or asking for directions; now, with just a few taps on our smartphones or GPS devices, we can access real-time navigation information, including traffic updates, estimated arrival times, and alternative routes. This location-based technology enhances not only personal travel but also impacts businesses that rely on efficient logistics, enabling them to optimize delivery routes and reduce costs.
Moreover, the integration of GPS technology into various applications has transformed how we interact with our surroundings. For instance, delivery services, ride-sharing apps, and even fitness trackers utilize GPS to provide valuable insights and streamline operations. Additionally, the rise of location-based services has allowed for personalized experiences, from recommending nearby restaurants to offering discounts based on geolocation. As we continue to embrace advancements in GPS and related technologies, we can expect our navigation capabilities to become even more intuitive and integrated into our everyday routines.
Counter Strike is a highly popular first-person shooter game that has captivated millions of players around the world. It is renowned for its tactical gameplay, teamwork, and competitive scene. Players can choose between two teams, Terrorists and Counter-Terrorists, to complete objectives or eliminate the opposing side. For those interested in finding the Top 10 airtag pet collars, this can help enhance their gaming experience by ensuring their pets are safe while they engage in thrilling matches.
The Science Behind GPS: Understanding Signals and Accuracy
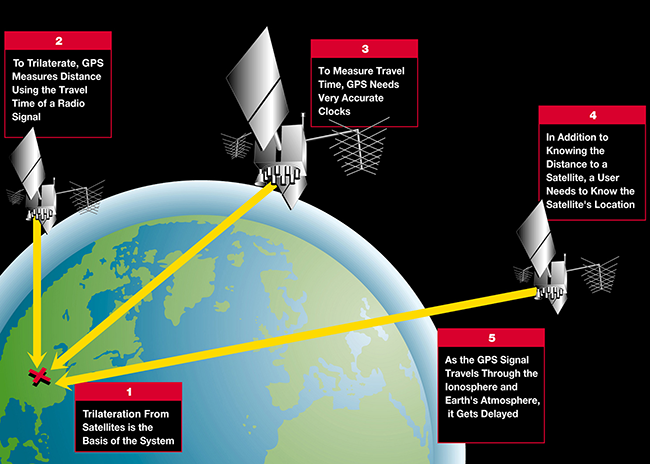
The science behind GPS involves a complex interplay of satellites, ground stations, and receivers that work together to provide accurate positioning data. At the heart of this technology are the signals transmitted by a constellation of at least 24 satellites orbiting the Earth. These satellites continuously broadcast their location and the precise time the signal was sent. When a GPS receiver on the ground picks up these signals, it calculates the distance from each satellite based on how long the signal took to arrive. With data from at least four satellites, the receiver can determine its own location in three-dimensional space: latitude, longitude, and altitude.
The accuracy of GPS can be influenced by various factors, including atmospheric conditions, signal obstructions, and the quality of the receiver. For instance, signals can be delayed when passing through the ionosphere or obstructed by buildings and trees. In open areas, GPS can achieve accuracy levels of better than 5 meters, while advanced techniques such as Differential GPS (DGPS) can enhance accuracy to within 1 meter or less. It's also important to note that GPS technology is constantly evolving, with new systems and methods being developed to further improve precision and reliability.
Frequently Asked Questions About GPS: How Does It Really Work?
Global Positioning System (GPS) technology has become an integral part of our daily lives, enabling navigation, mapping, and tracking services. At its core, GPS relies on a constellation of satellites orbiting the Earth, typically numbering around 24 active satellites. These satellites continuously transmit signals containing their location and the exact time the signal was sent. A GPS receiver, like those found in smartphones or dedicated navigation devices, picks up these signals from multiple satellites. By calculating the time it took for the signals to arrive, the receiver can determine its distance from each satellite and, using a method called triangulation, pinpoint its geographical location on Earth.
One common question about GPS is, how accurate is it? GPS is designed to provide location accuracy within 10 meters for civilian use, although advancements in technology can improve this accuracy to within a few centimeters for military and specialized applications. However, several factors can affect this accuracy, including atmospheric conditions, obstacles like tall buildings or trees, and satellite geometry, which refers to the positioning of the satellites in relation to the receiver. Overall, GPS remains an essential tool for navigation and location services, driving its continued evolution and integration into various technologies.